SoftWright is the developer of the Terrain Analysis Package - TAPtm- for Windows W2K/XP PC-based software to perform evaluation of existing or proposed radio transmitter sites; radio coverage predictions, intermodulation studies and radio transmitter site administration; TV and FM broadcasting, MMDS, ITFS, PCS, SCADA, WLL, WiFi, WiMAX, microwave, cellular, paging, air-to-ground, ship-to-shore and conventional two-way radio system design. The Version 6.0 of the Terrain Analysis Package (TAP) for Windows W2K/XP consists of twenty-five modules that, when combined together, are tools that bring a broad capability of RF system design to your personal computer. Most studies are accessed through one of two main screens - HDPath and HDCoverage. Presentation quality coverage calculations made in HDCoverage may be displayed and printed as maps with extensive individualized configuration by using the HDMapper screen.
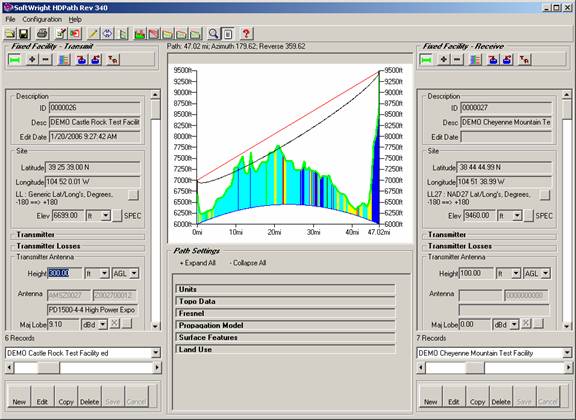
HDPath allows you to do exhaustive studies of paths from one screen. (click here for video)
HDPath is our completely new rf software for point-to- point path design. Select or key in any two fixed facilities and instantly see the details of the path. Studies such as reflection analysis, antenna heights, path clearances, and shadow studies are all done within this one screen, assuming you have licensed the appropriate software modules Learn More about HDPath
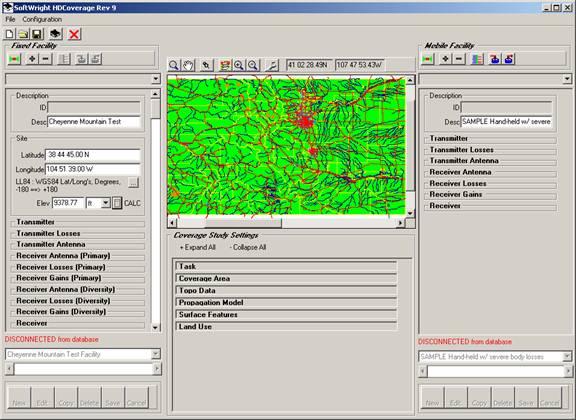
HDCoverage allows you to perform all coverage map calculations from one single screen.
HDCoverage is the easier way to calculate coverage maps for wireless applications. HDCoverage allows you to access everything you need to calculate an rf coverage map from one screen. All licensed propagation modules may be configured from this screen. On the left side of the screen you have access to the fixed facilities database for transmitting details. On the right side you have access to configure the receiving facilities. You can also graphically select the area on the map where you wish to perform coverage analysis. Learn More about HDCoverage

After Coverage Calculations are made in HDCoverage, the maps may be displayed with multiple layers in HDMapper.
The most fundamental module is the Basic Mapping Module. Basic Mapping will prepare path profiles with path line of sight and Fresnel Zone plots as well as HAAT calculations. For more sophisticated RF work you must add the RF Facilities Module and one or more of the TAP specialty modules. The benefits of each individual module are outlined below. We encourage you to read through the descriptions below and select the combination of modules that best suits your needs. For several examples of typical configurations of modules, click here. If you click "Contact Me" below and provide us some information, we will be happy to prepare a specific proposal for you.
Basic Mapping Module
The Basic Mapping Module is the foundation module of the Terrain Analysis Package (TAP) for Windows W2K/XP. The HDMapper (Hi-Definition Mapper) window in the Basic Mapping Module allows you to display geographic coordinates by moving the mouse over a map of the proposed coverage study. In addition to the displaying predicted coverage, you may include an unlimited number of layers of other information to be plotted. TAP 5 supports ESRI shapefiles, which have become the de facto standard of the GIS industry. Shapefiles can contain roads, street routings, civil boundaries, rivers and virtually any other type of geo-referenced data including data associated with that location such as population.
Included in the purchase of your TAP software will be a library of many shapefiles for the US. County boundaries, railroads, rivers and principal roads for the 50 US states are included. Each of these files is plotted in individual layers on the map. They can be easily turned on and off and moved to different orders to give great flexibility in the presentation of the results. Text can be easily added, edited and moved around the map.
You can move the mouse cursor over the map and read the geographic coordinates of the location of the cursor on the map. A completely new interface provides a simplified calculation and plot of the talk-back coverage area. You can also import and plot actual geo-referenced measured field strength data into the map window to be plotted with your predicted values. Given a distance and bearing from the designated site, you can compute the latitude and longitude of the end-point of the path. Conversions between geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) and Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) coordinates are provided. Bi-directional conversion between NAD27 and NAD83 is also supported.
This module provides access to SoftWright's TAP binary topographic data files, Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), derived from USGS 3-second, NGDC 30-second data, USGS 30 meter data and the new NED 1-second and 1/3-second data, as well as Defense Mapping Agency (DMA) Digital Terrain Elevation Data (DTED) files with 3-second, 30-second and 1-second resolutions. The SRTM (Space Shuttle) data files are also supported throughout the world. You can also export an ASCII file of geographic area elevation data to be used with the optional 3D Display module to draw the terrain in 3D.
Path profiles can be drawn showing elevations for the complete path. You can select any two points on a TAP map window and automatically plot a quick terrain profile between the points. You can also directly enter the exact geographic coordinates of both end points and plot a profile. Elevation values can be adjusted for any effective earth curvature value, including a "flat" earth. Radio path geometry studies can include line of sight and Fresnel zone plots for any combination of frequencies, antenna heights, Fresnel zone ratios and numbers, etc. Knife-edge diffraction losses, if present, are instantly calculated and displayed as you move the mouse across the plot of the path profile.
The Basic Mapping Module is the foundation module required for all TAP systems that do received signal level calculations. It can stand alone or may be used in conjunction with the many other modules described below. In order to calculate rf coverage maps you must have this module along with the RF Facilities Module listed below along with at least one propagation module.
RF Facilities Module
This module allows you to build up a database of both fixed location and mobile radio transmitting and receiving facilities. Here you can save templates of typical configurations of antennas, transmission line, transmitters and receivers to be recalled for use at a later date to save time in data entry when setting up your rf studies. This fixed facility database can also be populated directly from your imported data previously entered into EXCEL, Access or ASCII files as well as from FCC databases using the Facilities Exchange File Format fully supported by Percon Corporation. Using this module facilitates calculations to determine adequacy of received signal levels, taking into account receiver antenna gain and receiver system losses such as building and body losses. The RF Facilities Module provides not only a number of handy utilities but also the software hooks between the Basic Mapping Module's topo data reading and twenty-one other TAP specialty modules.
A large library of over 3300 directional antenna patterns from Celwave, Scala, Decibel and numerous other antenna manufacturers is included. If a specific pattern is not provided a newly-designed editor allows you to easily enter the antenna pattern information and retain it in a library for future use in coverage and link studies. Both azimuth and elevation patterns are used when available, permitting the accurate modeling of received signal levels close to the antenna and within the nulls of the pattern. User selected level and direction of beam tilt is fully supported. The TAP antenna pattern files can be printed as tabulations, and both the azimuth and elevation patterns can be plotted. You can import NSMA antenna pattern files, which are available from the FCC web site. In addition you can directly import manufacturer-supplied antenna pattern files from Celwave, Sinclair and Decibel and import and export antenna patterns to and from ASCII files.
A large library of transmission line types from several manufacturers including Andrew and Times Microwave is provided. For a selected coaxial cable or waveguide type, length and frequency, you can compute the percent efficiency, dB loss and power rating of the line.
The units conversion functions include the various units for field strength such as dBu/dBµV conversions as well as power density calculations, which are often required to demonstrate compliance with occupational safety requirements. The Free Space Field utility allows you to specify any two of the three parameters (power, distance, field strength) and the utility will calculate the third.
Propagation Modules
For area coverage maps you will need to select at least one of the following propagation modules in addition to the Basic Mapping Module and the RF Facilities Module. Each employs a separate and distinct method to calculate received field strength from a transmitter or repeater site. Each model has weaknesses and strengths. For a comparison of them check out Propagation Module Comparison Paper. Many engineers choose to have two or three different propagation models in their tool chest in order to compare predicted results and thereby greatly increase their confidence in predicted field strength. If you start with only one, we generally recommend Longley-Rice for land based communication applications. We recommend Bullington, if you are doing air to ground communications. Please read the article above and make an informed choice of what will best serve you needs. For each propagation model you can customize and standardize as many differently detailed parameter configurations as you want. We have a listed a few brief comments about each available propagation module below. If you wish to do analysis of possible interference with coverage from multiple sites you might also consider adding the optional Aggregate Coverage Module described below.
Longley-Rice Propagation Module
The Longley-Rice model is an implementation of many of the equations presented in the NTIA Tech Note 101. In addition to expected parameters such as frequency, effective radiated power (ERP), antenna pattern and antenna heights a number of other parameters unique to Longley-Rice are employed. These include such things as climate and soil conditions, ground conductivity and dielectric constant. The TAP program includes default values and suggested typical values to use if you do not have detailed information available for these constants. The program automatically calculates path elevations, effective antenna heights, horizon distances and terrain irregularity. Field intensity values are calculated at specified radial, tile or individual locations using basic median field and adjustments based on the Longley-Rice model.
Bullington Propagation Module
In the Bullington model computed free space field strength is adjusted for obstruction attenuation for knife-edge diffraction based on the method described in "Radio Propagation for Vehicular Communications" by Kenneth Bullington (IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, November 1977). Facility and path parameters (transmitter power, directional antenna, beam tilt, earth curvature correction, antenna heights, etc.) are all user-specified to provide maximum flexibility in system design. Bullington is widely used for link and land mobile coverage and is the best model for air to ground prediction. It computes field intensity values at specified radial, tile or individual locations, based on terrain data for a site and path, transmitter power, directional antenna, etc., using free space field and the Bullington obstruction loss method.
Okumura Propagation Module
The Okumura model computes basic median field strength and then adjusts for factors such as terrain, type of area (urban, suburban, open, etc.), terrain slope, etc. from the families of curves, as described in "Field Strength and its Variability in VHF and UHF Land-Mobile Radio Service", Review of the Electrical Communications Laboratory, Vol. 16, Numbers 9-10, Sep.-Oct, 1968, by Yoshihisa Okumura, et. al. The Okumura adjustments for area type, terrain slope, street orientation, etc., can be included or excluded individually from calculations. Facility and path parameters (transmitter power, directional antenna, beam tilt, earth curvature correction, antenna heights, etc.) are all user-specified to provide maximum flexibility in system design. Field intensity values are calculated at specified radial, tile or individual locations, based on terrain data for the site and path, transmitter power, directional antenna, etc., using basic median field and adjustments based on the Okumura method.
Rounded Obstacle Propagation Module
The Rounded Obstacle model is based on Section 7 ("Diffraction Over a Single Isolated Obstacle") of Tech Note 101(Transmission Loss Predictions for Tropospheric Communication Circuit, 1967, NTIS), treating path obstructions as rounded obstacles as described in Section 7.2. In addition, methods from Section 9 ("Forward Scatter") are used to compute tropospheric scatter losses. The two loss components may be combined in any of several user-selected methods. Some of the source code for the model was adapted from the program QZGBT used for protecting the rf noise floor at the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (Green Bank WV) radio astronomy site.
Broadcast/SMR (Part 73) Propagation Module
The Broadcast/SMR module of SoftWright's Terrain Analysis Package (TAP) uses topographic elevation information to compute height above average terrain (HAAT) from a specified site. This information is used to compute field strength from the f(50,50) and f(50,10) curves for FM and TV from Part 73 of the FCC Rules. Distances to a specified signal contour are calculated for SMR (specialized mobile radio) by appropriate deration of the Part 73 curves. It also calculates the f(50,90) field or contour for digital television filings in accordance with OET Bulletin No. 69, "Longley-Rice Methodology for Evaluating TV Coverage and Interference."
Carey Propagation Module
The Carey module uses topographic elevation information to compute height above average terrain (HAATs) from a specified site. This information is used to compute field strength from the f(50,50) and f(50,10) Carey curves from Part 22 of the FCC Rules. Distance to service contours for Cellular Geographic Service Area (CGSA) are also calculated, as well as the calculations described in FCC Report and Order 94-201. The Carey Module also allows calculation of the f(50,90) values based on f(50,50) adjusted according to Figure 5 from R-6406.
Hata/Davidson Propagation Module
The Hata/Davidson model uses developed empirical formulas derived from the many Okumura families of curves. The calculations depend upon which type of environment is present in the coverage area - urban, large city, small/medium size city, suburban or open area. Although Hata's model requires the inclusion of transmitting and receiving antenna heights it does not contain any of the path-specific corrections included in the more detailed Okumura Propagation model.
Egli Propagation Module
The Egli module is an implementation of John Egli's methodology published in October, 1957 in the Proceedings of the IRE. This model is derived from measured data out to a distance of approximately 50 miles and over gently rolling terrain with average hill heights of approximately 50 feet. It relies on frequency, distance and heights of transmitting and receiving antennas. It does not rely on localized path elevation data.
Additional Optional Modules to Consider
3D Display Module
The 3D Display module allows TAP to view coverage maps and other graphics draped over the three-dimensional surface of the terrain where it is calculated. Topographic maps and aerial photos may also be overlaid onto the surface. For full details click here.
Shadow Map Module
The Shadow Map Module identifies locations, which are 1) shadowed by terrain or obstructions, 2) locations which have line of sight, but obstructions within the 0.5 first Fresnel zone for a specific frequency, and 3) locations that have clear line of sight with no obstructions within the 0.5 first Fresnel zone. For specified transmit and receive antenna heights, you can plot the shadowed areas around a site. Using this tool will also greatly ease the location of unobstructed paths for distant receivers from a particular site for applications such as microwave and SCADA. Results are dependent upon antenna heights, frequency, terrain, obstructions and path geometry. Received field strength is not calculated within this module.

Pattern Distortion Module
The Pattern Distortion module will model the horizontal plane pattern distortion of a side mounted, vertically-polarized, omni-directional antenna when mounted on a metal tower structure. It uses the mounting orientation and distance from the tower, as well as the size and type of tower, frequency and nominal gain. This modeled pattern can then be plotted and saved to your antenna pattern library and used later to improve accuracy when calculating area coverage.
TAP Pattern Distortion modeling will calculate horizontal plane antenna pattern distortion present when a vertically polarized omni-directional antenna is side-mounted on a metal tower.
Stacked Antenna Module
The Stacked Antenna module will add multiple vertically-stacked horizontal plane directional antenna patterns (with different powers and major lobe azimuths) and calculate an approximate composite pattern. Propagation modules can use this resultant antenna pattern for computing field strength values. It is not to be used with horizontal arrays.
Aggregate Coverage Module
The Aggregate Coverage module takes the TAP propagation module results from multiple area coverage studies and calculates a new resultant area coverage. This aggregate coverage reflects the combination of multi-site and/or multi-frequency area coverages in a particular region to provide best server net coverage, as well as Simulcast Delay Spread (SDS) coverage. Areas of specific carrier to interference levels (C/I) may be calculated with this module and plotted. A very flexible Composite Study option will calculate the maximum or best server studies from any combination of any previously calculated individual coverage studies.
Map Crossing Module
Given a set of transmitter and receiver geographic coordinates, the Map Crossing module will calculate distance and bearing, crossing points on the maps and a list of required topographic maps (if the path is in the US). This greatly facilitates the preparation of paper maps for a field inspection of a proposed or problematic path. The module supports multiple map scales, calculates corner coordinates for all maps on path, calculates distance from corner coordinates to plot entrance and exit of path on map and calculates path distance at point of crossing.
Microwave Reliability Module
The Microwave Reliability module provides a flexible, easy-to-use tool for designing and evaluating microwave link reliability. It provides calculations of various models of rain attenuation up to 100 GHz, air absorption, path climate and terrain factors, fade margin, reliability, outage, frequency and space diversity improvement. Performance can be calculated for both digital and analog links. Using the flexibility of the RF facilities database in TAP, transmit and receive sites can be evaluated in different combinations of locations and equipment configurations to find the best design for each site and the best overall route for multiple site installations. You can print summaries of various site equipment configurations and path parameters to document the design process and the predicted reliability of the proposed facilities.
Antenna Elevation Module
The Antenna Elevation module will calculate a suitable antenna elevation above ground level for both transmit and receive antennas for a fixed point radio link using user-specified criteria at both ends and along the path. You can design for clearance of any ratio of any Fresnel zone plus an additional specified clearance if desired. You can fix the transmit end and then calculate the minimum receive antenna height. You can also define a possible range of transmit antenna heights and calculate the resulting receiving heights. It will allow you to select a particular combination of antenna heights and then will link to the Basic Mapping Module and plot the selected combination of antenna heights on the path profile.
Reflection Analysis Module
The Reflection Analysis module will locate potential reflection points along a path and evaluate the potential destructive interference on the received signal. For each point along the path, the antenna heights and path elevation at the point are used with Figures 7A and 7B from Lenkurt. The reflection point distance for that path elevation is determined for both 2/3 (Figure 7A) and 4/3 (Figures 7B) earth curvature.
VHF/UHF Reliability Module
The VHF/UHF Reliability module provides a flexible, easy-to-use tool for designing and evaluating link reliability in both UHF and VHF bands. It provides calculations of received signal level and fade margin. Using the flexibility of the RF facilities database in TAP, transmit and receive sites can be evaluated in different combinations of locations and hardware configurations to find the best design for each site and the best overall route for multiple site installations. Several propagation models calculate received field strength and you can select the calculation that you believe is the most realistic prediction for the path. With this module you can print summaries of various site equipment configurations and path parameters to document the design process and the predicted fade margin of the proposed facilities.
AutoPath Module
The AutoPath module enables TAP to automate setting up path specifications eliminating manual data entry. The program can then plot a path profile for each specified path, as well as compute the field strength value at the end of the path. You can define path information from a single transmitter site, or for a different transmitter site for every path. The path information (end point coordinates, antenna heights, earth curvature, transmitter ERP, etc.) can be entered manually into TAP, or you can import the values from another source, such as an Excel spreadsheet or Access database.
Land Use Module
The Land Use module enables you to import USGS Land Use Land Cover (LULC) files and then use them in the analysis of your radio coverage predictions and link designs. You can define loss values for any frequency ranges for each specified type of land use to permit the inclusion of very localized environmental conditions in predicted system performance. For areas in the continental US (excluding AK and HI) we can supply an optional prepared database on CD-ROM. For other areas the software facilitates your preparation of your own LULC database to be used in the software.
Topo Utilities Module
The Topo Utilities module will import USGS formatted ASCII files in their 3" and 30 meter DEM resolutions and convert them to the TAP binary format for use in TAP. An editor for TAP binary formatted topo data files (30", 3" and 30 meter) will allow you to modify the contents of these files to make individual corrections of anomalies in these files. A viewer will allow you to graphically view any of these TAP binary formatted files one at a time.
Intermodulation Products Module
The Intermodulation Products module is used to compute intermodulation products as a function of frequencies and other transmitter and receiver specs you enter manually or import from your own database. After executing your study, run the intermod report generator to filter and sort your results in order to isolate intermod problems that are likely to occur. See more details about the Intermodulation Products module.
Asset Manager Module
The Asset Manager can operate stand alone but will share the data already stored in the RF Facilities Fixed Facility Database on all your equipment. You can organize the technical information, maintenance schedules, equipment inventory including details such as serial numbers, space rental contracts, FCC license expiration dates, digital photos and a multitude of other items. See more details about the Asset Manager.
Minimum Hardware Recommendations
Windows W2K/XP with 256 MB ram minimum. Both Microsoft DirectX and .NET must be installed. (Note: Windows 95 /98 and NT are not supported.
700 MHz Pentium minimum (with graphical hardware acceleration supporting DirectX version 9 is also required)
Approximately 1.0 GB disk space minimum
CD-Rom drive Because TAP performs intensive engineering calculations, more ram and increased processor speed will be beneficial.
--
Ahmad Fahrudin
http://blog.fahrudin.web.id
http://friendster.com/fahroe
http://fahroe.wordpress.com
http://fahruddin.blogspot.com









No comments:
Post a Comment